Comparación basada en simulación de controladores ADRC, PI y PID en un convertidor SEPIC: rendimiento y complejidad
Palabras clave:
Convertidor SEPIC, ADRC, PI; PID;, Rechazo de perturbaciones, Sistemas de fase no mínima, Control de tensión, Control de sistemas de potencia, SimulaciónContenido principal del artículo
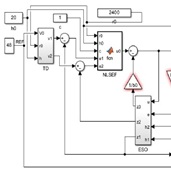
Introducción: los convertidores SEPIC son ampliamente empleados en electrónica de potencia por su capacidad de elevar o reducir voltajes. Sin embargo, su naturaleza no lineal y la presencia de un cero en el semiplano derecho dificultan el diseño de controladores rápidos y estables. Esta investigación analiza el desempeño de tres estrategias de control aplicadas a un convertidor SEPIC: Active Disturbance Rejection Control (ADRC), Proporcional–Integral (PI) y Proporcional–Integral–Derivativo (PID).
Objetivos: comparar el seguimiento de referencia, el rechazo de perturbaciones y la complejidad de implementación de los controladores ADRC, PI y PID en un convertidor SEPIC de corriente continua.
Materiales y métodos: se realizaron simulaciones en MATLAB/Simulink introduciendo perturbaciones en la fuente y en el voltaje de salida. Los índices IAE, ITAE, ISE e ITSE se emplearon para cuantificar precisión, rapidez y robustez. También se analizó el efecto de los parámetros de sintonización del ADRC, como el ancho de banda del observador y la velocidad del diferenciador de seguimiento.
Resultados: el ADRC presentó la respuesta más rápida y mejor rechazo de perturbaciones, aunque con oscilaciones inherentes y mayor complejidad de diseño. El PI logró un equilibrio entre simplicidad y desempeño, mientras que el PID tuvo la respuesta más lenta pero más suave ante perturbaciones.
Conclusiones: el ADRC es adecuado para aplicaciones que exigen control rápido y robusto. No obstante, el PI y el PID siguen siendo alternativas válidas cuando se prioriza la simplicidad o la suavidad en la señal de control.
Abolghasemi M, Soltani I, Shivaie M, Vahedi H. Recent advances of step-up multi-stage DC-DC converters: A review on classifications, structures and grid applications. Energy Reports. 2025;13:3050-81. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.egyr.2025.02.025 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.egyr.2025.02.025
Wang R, Feng W, Nordman B, Gerber D, Li Y, Kang J, et al. Technology standards for direct current microgrids in buildings: A review. Renew Sustain Energy Rev. 2025;211:115278. doi:
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2024.115278 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2024.115278
Venkatesan M, R N, Kacor P, Vrzala M. Bidirectional wireless power transfer: Bridging electric vehicles and the grid through converter analysis, coil topologies, and communication protocol review. Results Eng. 2025;25:103803. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rineng.2024.103803 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rineng.2024.103803
Yadav A, Verma A. Sepic DC-DC Converter: Review of Different Voltage Boosting Techniques and Applications. 2020;733-9. doi: https://doi.org/10.1109/ICIMIA48430.2020.9074897 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/ICIMIA48430.2020.9074897
Nazlıgül H, Mert ME, Edis C, Demir BN, Gurdal Y, Elattar KM, et al. Experimental and computational study of a solar-powered electrolysis system with a SEPIC converter for green hydrogen production. Sol Energy. 2025;298:113664. doi:
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.solener.2025.113664 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.solener.2025.113664
Khather S, A. Ibrahim M. Modeling and simulation of SEPIC controlled converter using PID controller. Int J Power Electron Drive Syst. 2020;11:833-43. doi:
https://doi.org/10.11591/ijpeds.v11.i2.pp833-843 DOI: https://doi.org/10.11591/ijpeds.v11.i2.pp833-843
Han J. From PID to active disturbance rejection control. IEEE Trans Ind Electron. 2009;56(3):900-6. https://doi.org/10.1109/TIE.2008.2011621 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/TIE.2008.2011621
Tu YH, Wang RF, Su WH. Active Disturbance Rejection Control-New Trends in Agricultural Cybernetics in the Future: A Comprehensive Review. Machines. 2025;13(2).
https://doi.org/10.3390/machines13020111 DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/machines13020111
Fareh R, Khadraoui S, Abdallah MY, Baziyad M, Bettayeb M. Active disturbance rejection control for robotic systems: A review. Mechatronics. 2021;80:102671. doi:
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mechatronics.2021.102671 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mechatronics.2021.102671
The MathWorks Inc. 2024. 2024 [cited 2025 Jun 15]. Design Active Disturbance Rejection Control for SEPIC Converter. Available from:
https://la.mathworks.com/help/slcontrol/ug/design-adrc-for-sepic-converter.html
Awad N, Humaidi A, Al-Araji A. Modified Tracking Differentiator for Enhancing the Performance of Exoskeleton Knee System Based on Active Disturbance Rejection Control. Univ Baghdad Eng J. 2023;23:69-83. https://doi.org/10.33103/uot.ijccce.23.1.6 DOI: https://doi.org/10.33103/uot.ijccce.23.1.6
Kumar P, Ajmeri M. Active Disturbance Rejection Control of a SEPIC Converter. Shaw RN, Siano P, Makhilef S, Ghosh A, Shimi SL, editors. Innov Electr Electron Eng. 2024;367-80. doi:
https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-99-8289-9_28 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-99-8289-9_28
Kumar P, Ajmeri M. Robust control of a single-ended primary inductor converter using adrc technique. Eng Res Express. 2023 Dec;6(1):15010. doi: https://doi.org/10.1088/2631-8695/ad153e DOI: https://doi.org/10.1088/2631-8695/ad153e
Patarroyo-Gutierrez LD, Gonzalez-Niño ME, Plazas JA. SEPIC Converter: Modeling and Control Considering Internal Energy Losses. Ing y Compet. 2024;26. doi:
https://doi.org/10.25100/iyc.v26i1.13016 DOI: https://doi.org/10.25100/iyc.v26i1.13016
LIU C, LUO G, CHEN Z, DING X. Overview on active disturbance rejection control for electro-mechanical actuation servo drive. Chinese J Aeronaut. 2025;38(7):103292. doi:
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cja.2024.11.002 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cja.2024.11.002
Herbst G, Madonski R. Active Disturbance Rejection Control: From Principles to Practice. 2025. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-72687-3 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-72687-3
Tian G, Gao Z. Frequency Response Analysis of Active Disturbance Rejection Based Control System. 2007 IEEE Int Conf Control Appl. 2007 Oct;1595-9.
https://doi.org/10.1109/CCA.2007.4389465 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1109/CCA.2007.4389465
Herbst G. Transfer function analysis and implementation of active disturbance rejection control. Control Theory Technol. 2021 Feb;19(1):19-34. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11768-021-00031-5 DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11768-021-00031-5
The MathWorks Inc. Design Active Disturbance Rejection Control for Boost Converter [Internet]. 2025 [cited 2025 Feb 23]. Available from: www.mathworks.com/help/slcontrol/ug/design-adrc-for-boost-converter.html
Downloads

Esta obra está bajo una licencia internacional Creative Commons Atribución-NoComercial-CompartirIgual 4.0.
Los autores que publican en esta revista están de acuerdo con los siguientes términos:
Los autores ceden los derechos patrimoniales a la revista y a la Universidad del Valle sobre los manuscritos aceptados, pero podrán hacer los reusos que consideren pertinentes por motivos profesionales, educativos, académicos o científicos, de acuerdo con los términos de la licencia que otorga la revista a todos sus artículos.
Los artículos serán publicados bajo la licencia Creative Commons 4.0 BY-NC-SA (de atribución, no comercial, sin obras derivadas).