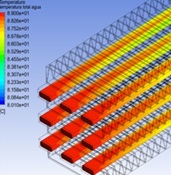
Heat transfer in a 4.1L engine radiator: experimental validation
Main Article Content
Introduction: The thermal performance of internal combustion engines largely depends on the efficiency of their cooling systems. Radiators play a fundamental role in dissipating the heat generated, ensuring proper engine operation. Optimizing radiator design using tools such as Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) improves heat transfer and reduces pressure losses, resulting in greater thermal efficiency and lower energy consumption. The geometry of tubes and fins is a key factor in this process, as it directly influences heat dissipation and pressure drop.
Objective: This study aims to analyze heat transfer in a 4.1L internal combustion engine radiator by combining CFD simulations and experimental validation to evaluate its thermal performance and optimize its design.
Methodology: A CFD model with 9 tubes and 4 rows of fins was used, representing a commercial radiator with three columns of 28 tubes each. The k-ω SST turbulence model was applied, and simulations were performed in ANSYS Fluent. Numerical results were validated with experimental measurements in a test bench, where temperatures, pressures, and flow velocities were recorded.
Results: Experimental validation showed a difference of less than 5.8% compared to the simulation. An 18% improvement in heat transfer and a 12% reduction in pressure drop were achieved. The geometrical arrangement of tubes and fins proved to be a key factor in thermal efficiency, as small modifications can significantly enhance heat dissipation without increasing aerodynamic resistance.
Conclusions: The validated CFD model accurately predicts radiator thermal performance and optimizes its design. However, the study presents certain limitations, such as geometric simplifications and turbulence model selection, which could be improved in future research. It is recommended to explore advanced materials and hybrid configurations to enhance thermal efficiency. Furthermore, these findings can be applied to the design of radiators for electric and hybrid vehicles, where thermal management is crucial. This approach could be key in developing more efficient and sustainable radiators for the automotive industry.
- heat transfer
- CFD
- engine radiator
- thermal efficiency
- numerical simulation
Achaichia A, Cowell TA. Heat transfer and pressure drop characteristics of flat tube and louvered plate fin surfaces. Exp Therm Fluid Sci. 1988;1(2):147–57. https://doi.org/10.1016/0894-1777(88)90032-5. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/0894-1777(88)90032-5
Chen H, Liu Y, Zhang X. Enhanced heat transfer in finned-tube radiators with variable fin spacing: A numerical study. J Therm Sci Eng Appl. 2023;16(3):321-37. https://doi.org/10.1115/1.4057245. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1115/1.4057245
Dittus FW, Boelter LMK. Heat transfer in automobile radiators of the tubular type. Int Commun Heat Mass Transf. 1985;12(1):3–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/0735-1933(85)90003-X. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/0735-1933(85)90003-X
Ferraris W, et al. Single layer cooling module for A-B segment vehicles. SAE Tech Pap. 2015;April. https://doi.org/10.4271/2015-01-1692. DOI: https://doi.org/10.4271/2015-01-1692
Wang F, et al. Comprehensive evaluation of the performances of heat exchangers with aluminum and copper finned tubes. Int J Chem Eng. 2023;2023. https://doi.org/10.1155/2023/6666947. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1155/2023/6666947
Garelli L, Ríos Rodriguez G, Dorella JJ, Storti MA. Heat transfer enhancement in panel type radiators using delta-wing vortex generators. Int J Therm Sci. 2019;137:64–74. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijthermalsci.2018.10.037. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijthermalsci.2018.10.037
Jabbar A, Kadhim Z, Khalaf K. Effect of the tube material on the thermal performance of automobile (radiator) of cooling system. Wasit J Eng Sci. 2024;12:81-93. https://doi.org/10.31185/ejuow.Vol12.Iss3.553. DOI: https://doi.org/10.31185/ejuow.Vol12.Iss3.553
Krásný I, Astrouski I, Raudenský M. Polymeric hollow fiber heat exchanger as an automotive radiator. Appl Therm Eng. 2016;108:798–803. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2016.07.181. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2016.07.181
Najman OA, Khadhim ZK, Khalaf KA. Numerical investigation on enhancing heating performance in automotive radiator. 2022. https://doi.org/10.31185/ejuow.Vol10.Iss3.384. DOI: https://doi.org/10.31185/ejuow.Vol10.Iss3.384
Oliet C, Oliva A, Castro J, Pérez-Segarra CD. Parametric studies on automotive radiators. Appl Therm Eng. 2007;27(11–12):2033–43. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2006.12.006. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2006.12.006
Park KW, Pak HY. Flow and heat transfer characteristics in flat tubes of a radiator. Numer Heat Transf A Appl. 2002;41(1):19–40. https://doi.org/10.1080/104077802317221429. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/104077802317221429
Patel HV, Subhedar DG, Ramani B. Numerical investigation of performance for car radiator oval tube. Mater Today Proc. 2017;4(9):9384–89. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2017.06.190. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2017.06.190
Razzaghi, P., Ghassabian, M., Daemiashkezari, M., Abdulfattah, A., Hassanzadeh, H. & Ahmad, H. (2022). Thermo-hydraulic performance evaluation of turbulent flow and heat transfer in a twisted flat tube: A CFD approach. Case Stud Therm Eng. 2022. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.csite.2022.102107. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.csite.2022.102107
Vajjha RS, Das DK, Ray DR. Development of new correlations for the Nusselt number and the friction factor under turbulent flow of nanofluids in flat tubes. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2015;80:353–67. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2014.09.018. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2014.09.018
Zeeshan M, Nath S, Banja D. Numerical study to predict optimal configuration of fin and tube compact heat exchanger with various tube shapes and spatial arrangements. Energy Convers Manag. 2017;148:737–52. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enconman.2017.06.011. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enconman.2017.06.011
Sahel D, Ameur H, Mellal M. Effect of tube shape on the performance of a fin and tube heat exchanger. J Mech Eng Sci. 2020;14(2):6709–18. https://doi.org/10.15282/JMES.14.2.2020.13.0525. DOI: https://doi.org/10.15282/jmes.14.2.2020.13.0525
Zuñiga-Cerroblanco JL, Collazo-Barrientos J, Hernandez-Guerrero A, Hortelano Capetillo J. Thermal and hydraulic analysis of different tube geometries to improve the performance of an automotive radiator. Rev Ing Ind. 2020;11(4):13–23. https://doi.org/10.35429/JIE.2020.11.4.13.23. DOI: https://doi.org/10.35429/JIE.2020.11.4.13.23
Downloads

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
Authors grant the journal and Universidad del Valle the economic rights over accepted manuscripts, but may make any reuse they deem appropriate for professional, educational, academic or scientific reasons, in accordance with the terms of the license granted by the journal to all its articles.
Articles will be published under the Creative Commons 4.0 BY-NC-SA licence (Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike).